Scaling Large Language Models For Next-Generation Single-Cell Analysis
C2S‑Scale is our newest collaboration with Google Research and Google DeepMind. By pre‑training language models of up to 27 billion parameters on one billion+ tokens of “cell sentences,” biomedical text, and rich metadata, then fine‑tuning them with modern reinforcement‑learning techniques, we achieve state‑of‑the‑art predictive and generative performance on complex multicellular tasks. C2S‑Scale moves beyond cell‑level snapshots toward “virtual cells”—in‑silico avatars that enable researchers to run thousands of hypothetical experiments, accelerate therapeutic target discovery, and simulate patient‑specific responses long before a wet‑lab assay.
[Read the preprint →]
Abstract
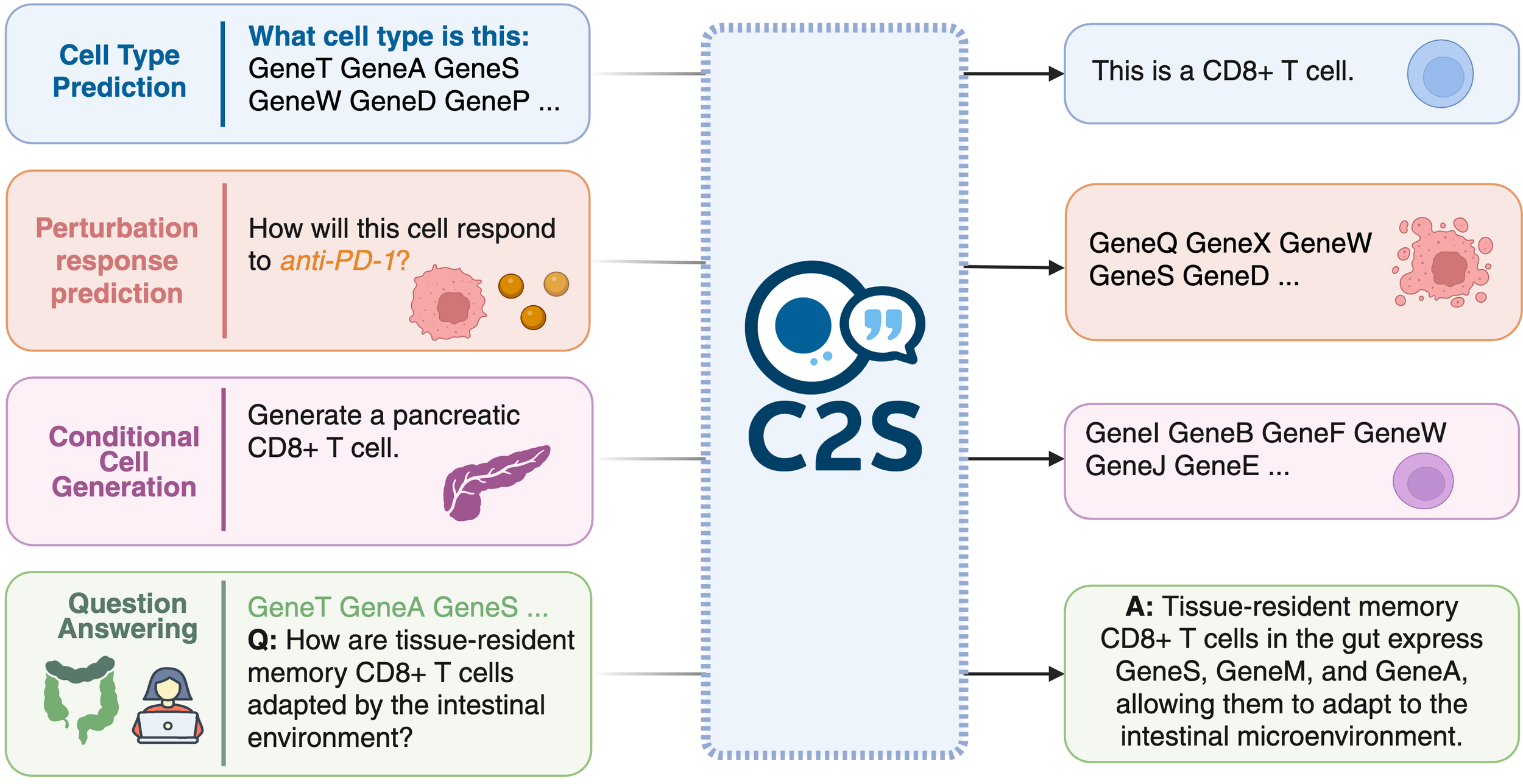
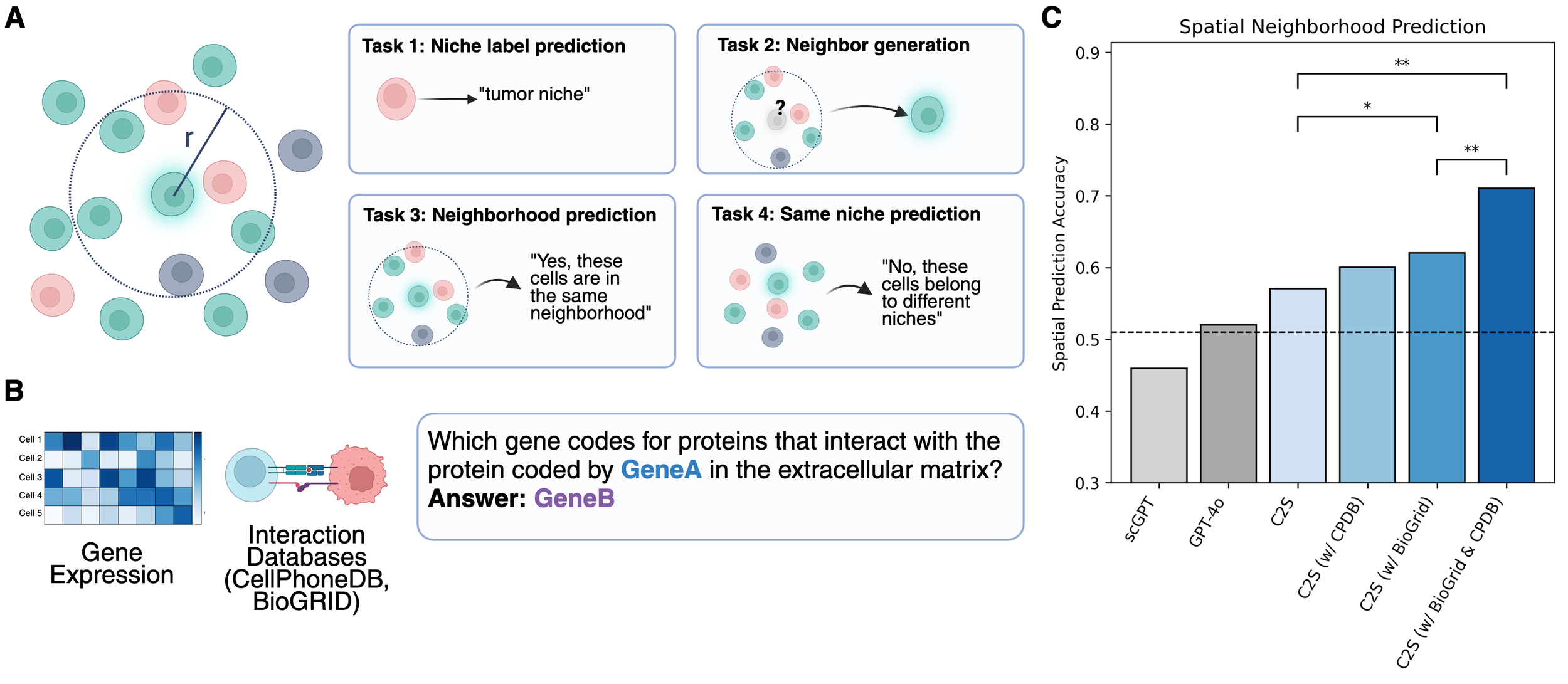
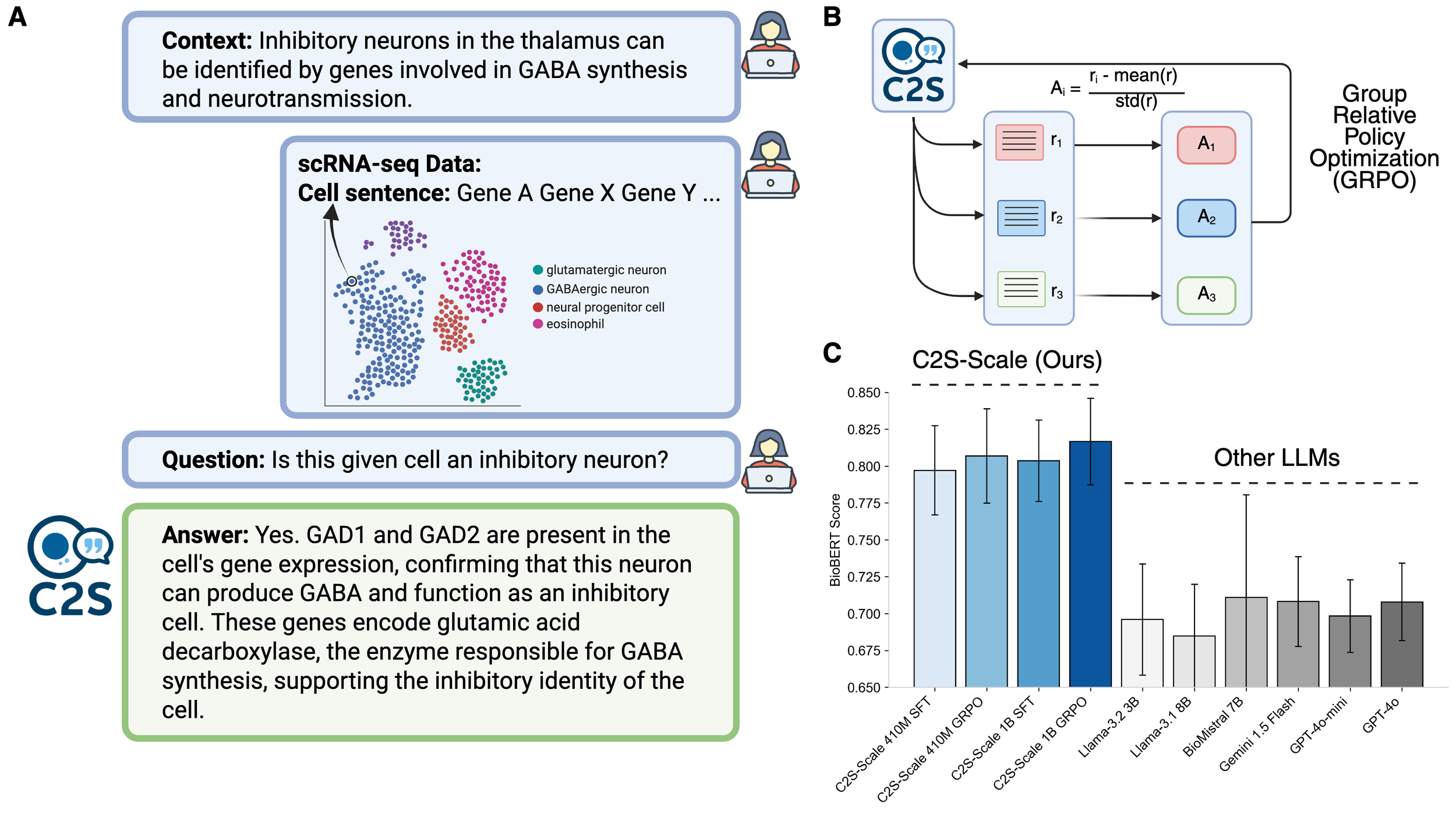
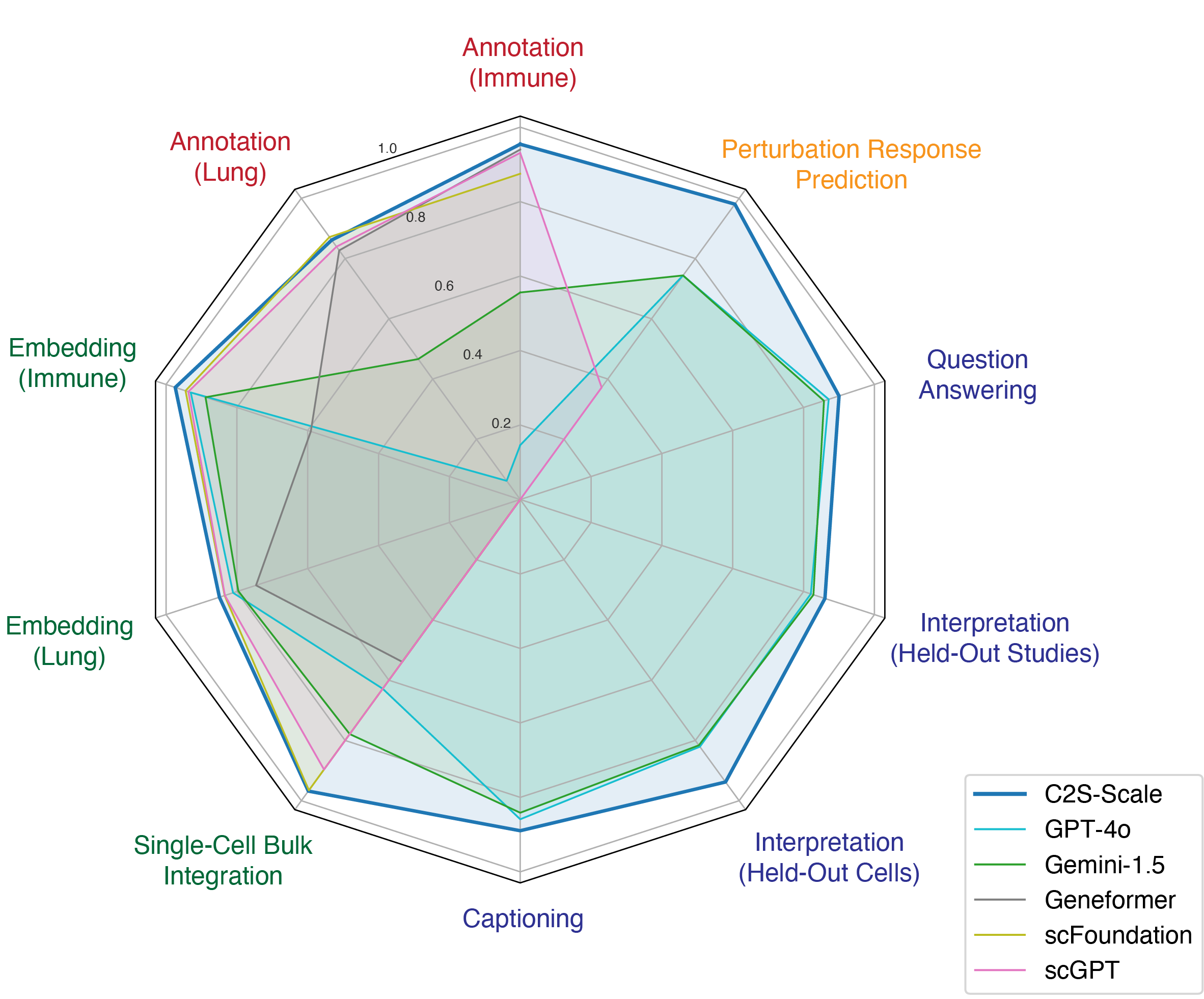
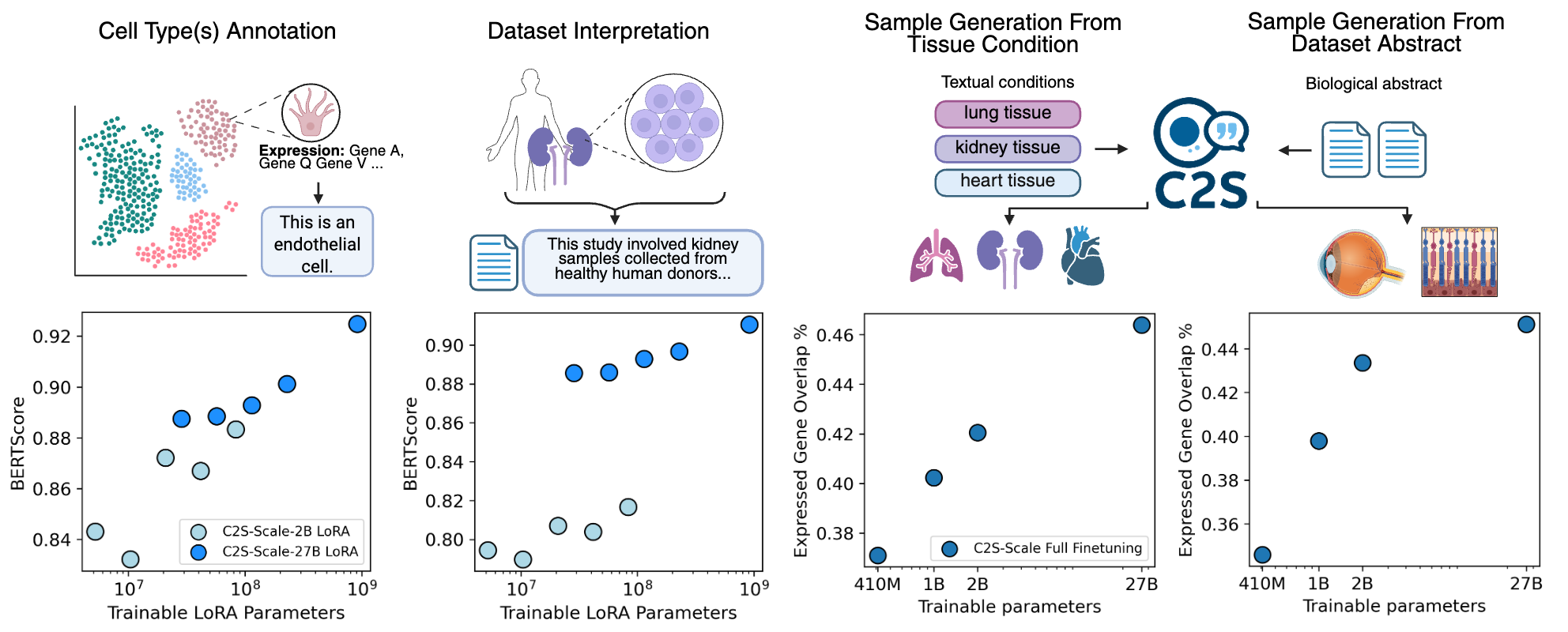
Single-cell RNA sequencing has transformed our understanding of cellular diversity, yet current single-cell foundation models (scFMs) remain limited in their scalability, flexibility across diverse tasks, and ability to natively integrate textual information. In this work, we build upon the Cell2Sentence (C2S) framework, which represents scRNA-seq profiles as textual ``cell sentences,'' to train Large Language Models (LLMs) on a corpus comprising over one billion tokens of transcriptomic data, biological text, and metadata. By scaling model size to 27 billion parameters, we observe consistent improvements in predictive and generative capabilities, as well as the capacity for advanced downstream tasks requiring synthesis of information across multicellular contexts. Through targeted fine-tuning supported by modern reinforcement learning techniques, our approach excels in tasks such as perturbation response prediction, natural language interpretation, and complex biological reasoning. By unifying transcriptomic and textual data at unprecedented scales, this approach not only surpasses both specialized single-cell models and general-purpose LLMs, but also establishes a powerful platform for next-generation single-cell analysis, paving the way for the development of “virtual cells.”
Author list
Syed Asad Rizvi*,†,1, Daniel Levine*,1, Aakash Patel*,1, Shiyang Zhang*,1, Eric Wang*,2, Sizhuang He, David Zhang, Cerise Tang, Zhuoyang Lyu, Rayyan Darji, Chang Li, Emily Sun, David Jeong, Lawrence Zhao, Jennifer Kwan, David Braun, Brian Hafler, Jeffrey Ishizuka, Rahul M. Dhodapkar, Hattie Chung, Shekoofeh Azizi2, Bryan Perozzi3, David van Dijk1,‡
*Equal contribution
†Work partially done during internship at Google Research
‡Corresponding author
1Yale University, 2Google DeepMind, 3Google Research